
Neuropathy, also known as peripheral neuropathy, is a broad term that is used to describe damage to the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. There are over 100 types of peripheral neuropathy that can be classified into four categories, with each type having their own symptoms and prognosis. In this article, we’ll discuss the types of peripheral neuropathy and its connection to amyloidosis.
Symptoms
One of the challenges with neuropathy is the fact that symptoms can vary significantly based on what nerve is damaged. Additionally, symptoms can develop over the course of months to years (chronic neuropathy) or come on suddenly (acute neuropathy). Some of the most commonly seen symptoms are listed below:
- Muscle weakness
- Cramps
- Muscle twitching
- Loss of muscle and bone
- Changes in skin, hair, or nails
- Numbness
- Loss of sensation or feeling in body parts
- Loss of balance or other functions as a side effect of the loss of feeling in the legs, arms, or other body parts
- Emotional disturbances
- Sleep disruptions
- Loss of pain or sensation that can put you at risk, such as not feeling an impending heart attack or limb pain
- Inability to sweat properly, leading to heat intolerance
- Loss of bladder control, leading to infection or incontinence
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting because of a loss of control over blood pressure
- Diarrhea, constipation, or incontinence related to nerve damage in the intestines or digestive tract
- Trouble eating or swallowing
- Life-threatening symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or irregular heartbeat
Types of Neuropathy
- Motor Neuropathy → Damage to the motor nerves control how you move.
- Sensory Neuropathy → Damage to sensory nerves control what you feel.
- Autonomic Nerve Neuropathy → Damage to autonomic nerves that control functions that are involuntary (ie. you do not consciously control).
- Combination Neuropathies → Damage to a mix of 2 or 3 of these other types of neuropathies. For example, damage to both sensory and motor nerves would result in sensory-motor neuropathy.
Amyloidosis
Peripheral Neuropathy is one of the hallmarks of amyloidosis, often seen in the transthyretin form of amyloidosis (ATTR). ATTR-PN, or transthyretin amyloid polyneuropathy, is a disease where the transthyretin protein becomes unstable and misfolds. This unstable protein (“amyloid”) then deposits in the nerve tissue, resulting in damage to these nerves. While amyloid deposits primarily in the peripheral nerves, it is not uncommon for amyloid deposition in the autonomic nerves as well.
While peripheral neuropathy is most commonly associated with ATTR amyloidosis, it should be noted that peripheral neuropathy is also seen in 15-35% of patients with AL amyloidosis.
Most importantly, these are the most common and important signs and symptoms to be aware of, in order to diagnose ATTR amyloidosis.
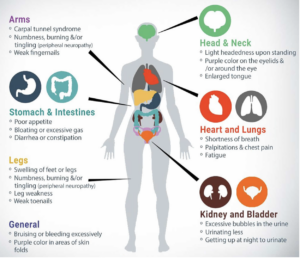
Neurological Complications of ATTR Amyloidosis
Patients with ATTR amyloidosis are commonly faced with neurological complications. In this presentation, Dr. Chafic Karam from the University of Pennsylvania goes through four areas: an overview of the neurological systems, how amyloid damages the nerves, neurological signs of ATTR amyloidosis, and how to detect amyloid and diagnose ATTR amyloid neuropathy.
===========================================================
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14737-neuropathy
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/peripheral-neuropathy
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061
https://practicalneurology.com/articles/2021-july-aug/neuromuscular-amyloidosis
https://healthjade.net/familial-amyloidosis/