Hereditary Amyloidosis in Black Americans of African Descent: ATTR V122I Variant
Amyloidosis, still considered a relatively rare disease, can take several forms. Each slightly different, but most sharing similar debilitating symptoms of cardiac and/or neurological impairment, or both. It is viewed by many experts that amyloidosis has been presenting in plain sight and missed, or wildly underdiagnosed, for decades and, in some cases, generations. Thankfully, education to raise awareness within the healthcare community, along with improvements in diagnostic tools and testing, the journey to diagnosis and treatment is becoming more visible.
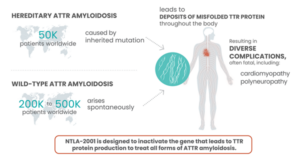
The hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (hATTR) type results from a genetic mutation of a protein, transthyretin, which is produced in the liver and circulates throughout the body. The mutation causes the TTR protein to misfold, becoming unstable and depositing in organs and nerve systems causing impairment and eventual organ failure. Common symptoms for the disease include bilateral carpel tunnel syndrome, muscle weakness, cardiomyopathy, polyneuropathy, GI issues especially chronic diarrhea and constipation, and both nuisance and serious concerns and if untreated can lead to death. Early diagnosis, genetic testing to identify the exact genetic mutation, and treatment are important to slow the progression of the disease and conserve quality of life.
SIGNIFICANTLY UNDER-DIAGNOSED
Considered a rare disease, advances in diagnosis have shown that it is less rare than originally thought.
Familial amyloidosis caused by a transthyretin mutation occurs in approximately 1 in 100,000 Caucasians in the U.S, and more commonly in African Americans (approximately 4% in that population). This condition is prevalent in Portugal, Sweden, Japan, Ireland, Spain, France, Finland, Germany and Greece. Symptoms usually begin between 40 and 65 years of age.
https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/amyloidosis/
To date over one hundred variants of TTR have been identified as causing ATTR amyloidosis and they are distributed worldwide with concentrations in various ethnic populations. One variant, V122I is most commonly found in people with African and especially West African ancestry. It has been distributed worldwide but especially in North America and the Caribbean through historic slave trade and the migration of populations. This variant is most often associated with ATTR-CM (Amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy) and heart failure.
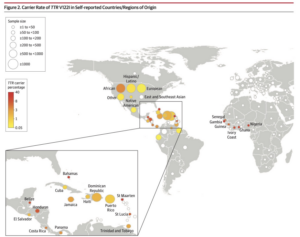
Worldwide Carrier Rates of TTR V122I in Self-Reported Countries/Regions
From Multicenter Study JAMA 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2191-2202.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17935.
In an article by J. Buxdaum and F. Ruberg in the Journal Genetics in Medicine January 2017, the authors stated the following findings.
Since the identification of a valine-to-isoleucine substitution at position 122 (TTR V122I; pV142I) in the transthyretin (TTR)-derived fibrils extracted from the heart of a patient with late-onset cardiac amyloidosis, it has become clear that the amyloidogenic mutation and the disease occur almost exclusively in individuals of identifiable African descent. In the United States, the amyloidogenic allele frequency is 0.0173 and is carried by 3.5% of community-dwelling African Americans. Genotyping across Africa indicates that the origin of the allele is in the West African countries that were the major source of the slave trade to North America. At autopsy, the allele was found to be associated with cardiac TTR amyloid deposition in all the carriers after age 65 years; however, the clinical penetrance varies, resulting in substantial heart disease in some carriers and few symptoms in others. The allele has been found in 10% of African Americans older than age 65 with severe congestive heart failure. At this time there are potential forms of therapy in clinical trials. The combination of a highly accurate genetic test and the potential for specific therapy demands a greater awareness of this autosomal dominant, age-dependent cardiac disease in the cardiology community.
Genet Med advance online publication 19 January 2017
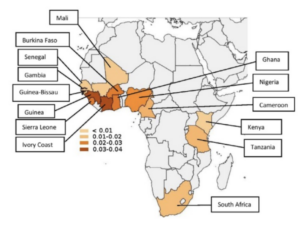
The prevalence and distribution of the amyloidogenic transthyretin (TTR) V122I allele in Africa.
1:CAS:528:DC%2BC28XhsFSlsbfJ 10.1002/mgg3.231 Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2016; 4: 548-556
Dr. Martha Grogan, director of the Cardiac Amyloid Clinic of Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota commented in an interview published in the Mayo News Network (https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/expert-alert-cardiac-amyloidosis-masquerades-as-other-conditions-1-type-affects-more-black-americans/) that amyloidosis can be tricky to suspect because symptoms may not be initially present and they may mimic other more common diseases. Currently there are options for free saliva or blood tests through several pharmaceutical companies. To determine the type of the disease genetic testing is important.
The University of Pennsylvania and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai conducted a study of 52,492 participants of which 11,143 were of self-reported African ancestry. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2757227
An excellent discussion of the results emphasizes the conclusion that a significant association of TTR V122I and heart failure in the tested population, primarily in those of West African ancestry, exists. In addition, they confirm previous studies that have suggested a high rate of underdiagnosis of hATTR-CM in cases of cardiomyopathy and heart failure in elderly patients of African Ancestry. The discussion further suggests that this is likely due to lack of information and familiarity with the disease in the medical community.
CITATION: Damrauer SM, Chaudhary K, Cho JH, et al. Association of the V122I Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis Genetic Variant With Heart Failure Among Individuals of African or Hispanic/Latino Ancestry. JAMA. 2019;322(22):2191–2202. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.17935. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31821430/
Discussion of a different study of 7,514 African American participants in the US considered the question of the association between genetic variation and the risk of heart failure. This study was conducted by the University of Alabama, University of Colorado, Columbia University, and Cornel University. The results are similar to those in the University of Pennsylvania study discussed above, with additional comments that more subtle symptoms and changes may be apparent well before the typical onset of significant disease, average age 65, and the need for earlier screening for early detection and treatment.
An autosomal-dominant disease, hATTR-CM has a median survival of nearly 2.5 years without treatment after receiving a diagnosis.34,35 Extrapolating the hATTR-CM–associated Val122Ile variant frequency to the population level suggests that approximately 1.4 million Black individuals carry this variant implicated in the development of heart failure and reduced overall survival. Despite the possible clinical implications, the Val122Ile TTR variant, which is seen relatively more commonly among individuals of African ancestry, is not included in the list of clinically actionable deleterious variants compiled by the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics.9 Thus, this potentially deleterious variant may not be reported as clinically actionable, thereby reducing physician vigilance for hATTR-CM.
Findings In this retrospective cohort study that included 7,514 Black participants in the US with a median 11.1 years of follow-up, the incidence of heart failure was 15.6 per 1000 person-years among Val122Ile variant carriers compared with 7.2 per 1000 person-years among noncarriers, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 2.43.
Meaning Being a carrier of the Val122Ile variant was significantly associated with an increased risk of heart failure among Black individuals living in the US.
CITATION: Parcha V, Malla G, Irvin MR, et al. Association of Transthyretin Val122Ile Variant With Incident Heart Failure Among Black Individuals. JAMA. 2022;327(14):1368–1378. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.2896
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35377943/
SUMMARY
Despite the evidence that a meaningful 3-4% of the US Black population of West African ancestry likely carries the V122I genetic mutation, hereditary TTR amyloidosis remains significantly underdiagnosed and undertreated in this population.
Cardiac symptoms in elderly black patients have too often been treated for more common cardiomyopathy and heart conditions, resulting in lack of appropriate treatment and often death. Because of lack of awareness in the medical community and reduced access to expert medical care, more subtle symptoms in younger black patients generally have not caused the physicians to consider amyloidosis. Additionally, lack of genetic testing can mean that entire families are unaware of the implications of the disease.
Amyloidosis can be devastating to both patients and their families. Increased awareness of the disease, availability of testing, and FDA-approved therapies are slowly beginning to shift this dynamic. However, there is still much work to be done to close the gap between diagnosed cases and the population estimated to be affected.
Early diagnosis is key.
For additional information regarding hereditary amyloidosis:
Worldwide Hotspots of Hereditary TTR Amyloidosis (ATTRv)
Hereditary Amyloidosis: T60A Variant