WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
Spinal stenosis is narrowing of the spinal column that causes pressure on the spinal cord, or narrowing of the openings (called neural foramina) where spinal nerves leave the spinal column.
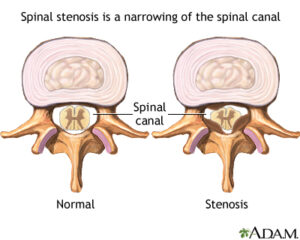
This can develop as you age from drying out and shrinking of the disk spaces. (The disks are 80% water.) The narrowing can cause compression on nerve roots resulting in pain or weakness of the legs. If this happens, even a minor injury can cause inflammation of the disk and put pressure on the nerve. You can feel pain anywhere along your back or leg(s) that this nerve supplies.1
SYMPTOMS1
Symptoms often get worse slowly over time. Most often, symptoms will be on one side of the body, but may involve both legs. Symptoms include:
- Numbness, cramping, or pain in the back, buttocks, thighs, or calves, or in the neck, shoulders, or arms
- Weakness of part of a leg or arm
Symptoms are more likely to be present or get worse when you stand or walk. They often lessen or disappear when you sit down or lean forward. Most people with spinal stenosis cannot walk for a long period. More serious symptoms include:
- Difficulty or poor balance when walking
- Problems controlling urine or bowel movements
A POTENTIAL CLUE TO AMYLOIDOSIS?
Amyloid is a very common finding in cartilage and ligaments of elderly subjects, and transthyretin has been demonstrated in some deposits. Lumbar spinal stenosis is also a condition of usually elderly individuals in whom narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal leads to compression of nerves to the lower limbs.
“Another very important historical clue is spinal stenosis, and actually that’s much more commonly seen in patients with ATTR than AL, and in fact, again, almost exclusively in wild type,” according to Dr. Mazen Hanna2
WHAT IS SENILE, AKA WILD-TYPE, AMYLOIDOSIS (ATTRwt)?
Amyloidosis is a generic name for a very diverse group of protein folding disorders, all characterized by creation of cross-beta-sheet fibrils. At least 30 different human proteins have been shown to form amyloid fibrils in vivo (7). Two main groups of amyloid conditions exist: systemic and localized. In the systemic conditions, deposits occur in many organs and tissues, and the diseases are usually life-threatening; in each of these diseases one out of at least 15 plasma proteins forms amyloid fibrils far from the place of parent protein synthesis. In the localized conditions, the proteins are expressed at the site of deposition (8). In both groups, fibrils usually deposit extracellularly and can form conspicuous masses that deform a tissue and interfere with its normal functions.5
Senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), derived from wild-type transthyretin (TTR), is common in association with aging, although symptom-giving disease usually is comparably rare and affects males at least 10 times more often than women. Restrictive cardiomyopathy is the main clinical expression. However, carpal tunnel syndrome is common in SSA, and widely spread wild-type ATTR amyloid deposits at other connective tissue sites have been demonstrated (25).5
Joint cartilage and ligaments are targets of both localized and systemic amyloid. Of the systemic forms, Aβ2-microglobulin [for nomenclature, see (7)] amyloidosis is well-known to engage skeletal and joint structures in patients under hemodialysis due to renal insufficiency (9-13). Also, immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis is known to generate a variety of symptoms from joints and skeleton, sometimes with neural lesions. Carpal tunnel syndrome is often noted in transthyretin (ATTR) and Aβ2-microglobulin amyloidosis (15–17).5
CONCLUSION
From the studies referenced therein, results suggest that transthyretin-derived amyloid deposits may occur more frequently in various ligaments and tendons than originally expected3 and that lumbar spinal stenosis quite frequently may be a consequence of senile systemic amyloidosis [also known as wild-type amyloidosis; ATTRwt]5.
Stay suspicious.
Sources:
1 https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/spinal-stenosis
2 https://www.neurologylive.com/view/cardiac-amyloidosis-management
3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21334722/
Sueyoshi T, Ueda M, Jono H, Irie H, Sei A, Ide J, Ando Y, Mizuta H. Wild-type transthyretin-derived amyloidosis in various ligaments and tendons. Hum Pathol. 2011 Sep;42(9):1259-64. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.11.017. Epub 2011 Feb 21. PMID: 21334722.
4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14640042/
Westermark P, Bergström J, Solomon A, Murphy C, Sletten K. Transthyretin-derived senile systemic amyloidosis: clinicopathologic and structural considerations. Amyloid. 2003 Aug;10 Suppl 1:48-54. PMID: 14640042.
5 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4116761/
Westermark P, Westermark GT, Suhr OB, Berg S. Transthyretin-derived amyloidosis: probably a common cause of lumbar spinal stenosis. Ups J Med Sci. 2014;119(3):223-228. doi:10.3109/03009734.2014.895786
6 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spinal_stenosis